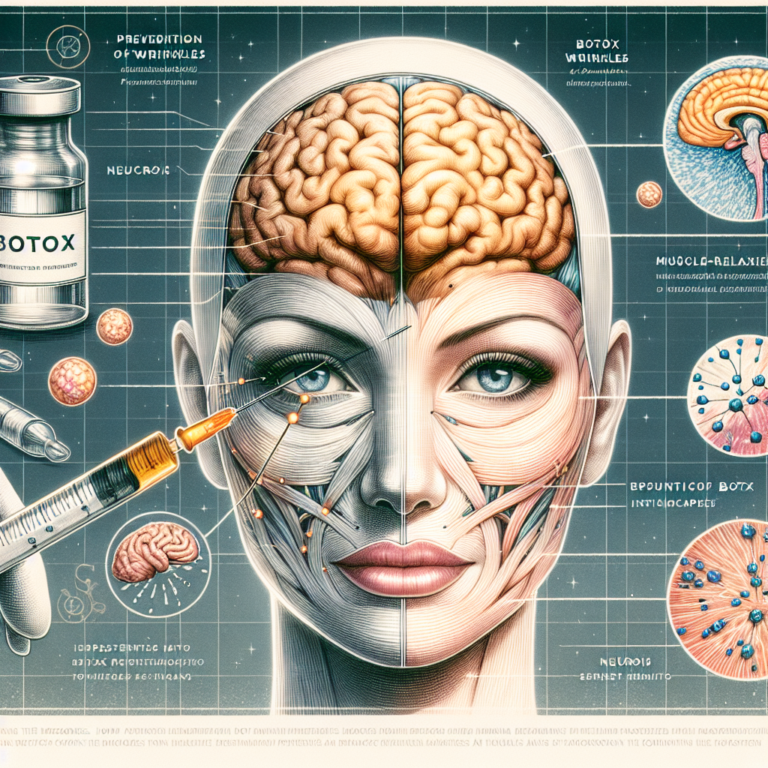
Exploring the Mechanisms: How Botox Prevents Wrinkles and Treats Medical Conditions
In recent years, Botox has transcended its initial reputation as a mere cosmetic treatment to become a multifaceted therapeutic agent with various applications. Originally approved by the FDA in 1989 for the treatment of strabismus (crossed eyes), Botox, or botulinum toxin type A, has garnered significant attention for its ability to reduce facial wrinkles. However, its mode of action also offers insights into its effectiveness in treating various medical conditions, from chronic migraines to muscle spasms. This article explores the mechanisms behind Botox’s popularity as both a cosmetic marvel and a medical remedy.
The Science Behind Botox
Botox is derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, which produces a neurotoxin that, in specific doses, can inhibit the release of acetylcholine—a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting nerve signals to muscles. By blocking the release of acetylcholine, Botox effectively paralyzes the targeted muscles, resulting in temporary muscle weakness or paralysis.
How Botox Prevents Wrinkles
The efficacy of Botox in wrinkle prevention, particularly in the upper face, is largely due to its ability to relax the muscles that contribute to wrinkle formation. Dynamic wrinkles, such as crow’s feet and frown lines, occur when facial muscles contract during expressions. Over time, these repeated contractions lead to permanent lines and wrinkles.
When Botox is injected into specific muscles, it limits their movement, resulting in a smoother appearance of the overlying skin. This process takes about three to seven days post-injection to fully manifest, with effects lasting approximately three to six months. Patients often describe the experience as a subtle softening of facial expression rather than a complete freeze, allowing for a more natural look.
Medical Applications of Botox
Beyond its cosmetic advantages, Botox’s therapeutic uses are extensive and varied. Here are some notable medical conditions commonly treated with Botox:
-
Chronic Migraines: Studies indicate that Botox can reduce the frequency and severity of chronic migraines. It is believed that the neurotoxin interferes with pain signaling pathways, leading to decreased migraine occurrence and intensity. Patients often report significant improvements after a series of injections.
-
Muscle Spasms: Botox has shown promise in treating spasticity caused by neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis and cerebral palsy. By injecting Botox into affected muscles, physicians can help reduce involuntary muscle contractions, providing relief and improving mobility.
-
Hyperhidrosis: Excessive sweating, or hyperhidrosis, can be both physically uncomfortable and socially embarrassing. Botox injections block the nerves responsible for activating sweat glands, offering an effective solution for patients suffering from this condition.
-
Overactive Bladder: For individuals with urinary incontinence or an overactive bladder, Botox can relax the bladder muscles, reducing the urgency and frequency of urination, which subsequently improves quality of life.
- Rhinitis and Nasal Congestion: Botox has also emerged as a treatment option for chronic rhinitis. By injecting the toxin into specific areas of the nasal cavity, it can reduce mucus production and alleviate congestion.
Conclusion
The mechanisms by which Botox operates unveil its extraordinary versatility. While its association with wrinkle reduction often steals the spotlight, its therapeutic capabilities represent a significant advancement in medical science. The implications of Botox extend beyond aesthetics, offering improved quality of life for patients with various health challenges. As ongoing research continues to uncover innovative applications, Botox may well redefine its role in both cosmetic and medical treatments, blurring the line between beauty and therapy.
As with any medical treatment, it’s crucial for patients to consult with qualified healthcare providers to understand the risks and benefits associated with Botox. In doing so, individuals can make informed decisions that align their cosmetic desires with their health needs.